Calvin cycle is known as C3 cycleas in the CO2 fixation stagethe CO2 diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplast in mesophyll cells and added to the five carbon acceptor ribulose-15-bisphosphate yielding a six-carbon intermediate product which is hydrated to produce two molecules of three-carbon 3-phosphoglycerate or phosphoglyceric acid 3-PGAas the first stable product. Why are C3 and C4 cycle called so.
Everything You Need To Know About The Calvin Cycle Biology Junction
The whole sequence of chemical reactions by which CO2 is assimilated ad reduced i the dark reaction of photosynthesis was investigated by MCalvin who named it C3 cycle also known as Calvin cycle or triose phosphate cycle there are certain steps involved in C3 cycle.

Why is calvin cycle called c3 cycle. The most common set of carbon fixation reactions is found in C3-type plants which are so named because the major stable intermediate is the 3-carbon molecule glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The Calvin cycle is called such because every process produces something that the next process needs right back to the original step. The most common set of carbon fixation reactions is found in C3-type plants which are so named because the major stable intermediate is the 3-carbon molecule glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Calvin or C 3 Cycle It is the basic mechanism by which CO 2 is fixed reduced to form carbohydratesIt was proposed by Melvin Calvin. Why is Calvin cycle called C3 cycle. Bassham used radioactive isotope of carbon C 14 in Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliques to determine the sequences.
The most common set of carbon fixation reactions is found in C3-type plants which are so named because the major stable intermediate is the 3-carbon molecule glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. C3 Pathway Calvin Cycle The majority of plants produce 3-carbon acid called 3-phosphoglyceric acid PGA as a first product during carbon dioxide fixation. In the Calvin cycle the 3 carbon molecule PGA is the first stable molecule to be produced.
The Calvin cycle CalvinBensonBassham CBB cycle reductive pentose phosphate cycle RPP cycle or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic. What is Reduction in the Calvin Cycle. These reactions best known as the Calvin cycle Figure 62.
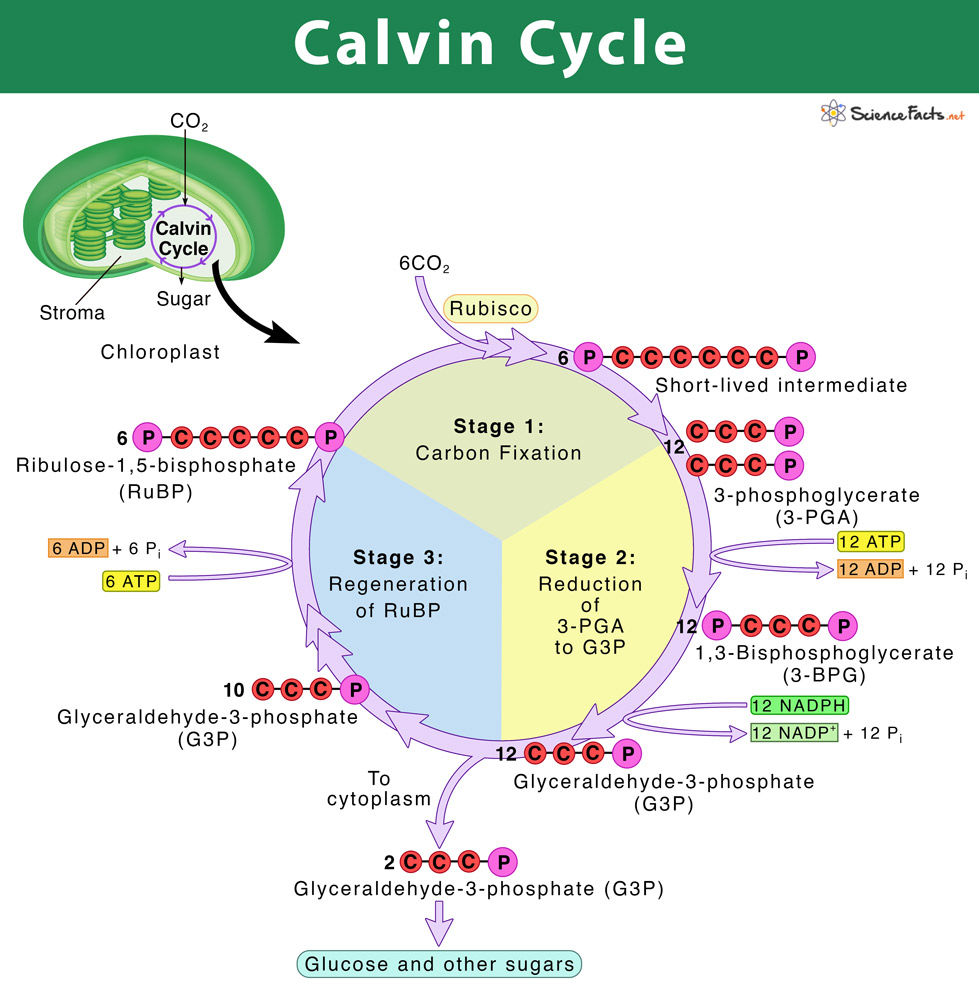
First about C3 cycle. The conversion of CO2 to carbohydrate is called Calvin Cycle or C3 cycle and is named after Melvin Calvin who discovered it. Overview of the Calvin cycle.
The Calvin cycle is an anabolic process a chemical reaction that synthesizes molecules in metabolism that builds the molecules required to make glucose a six-carbon sugar that is the product of reactions following the Calvin cycle. Why is the calvin cycle called C3 Photosynthesis. C4 plants are plants which cycle carbon dioxide to 4-carbon sugar compounds in order to enter the C3 or the Calvin cycle.
The cycle was discovered in 1950 by Melvin Calvin James Bassham and Andrew Benson at the. Calvin or C3 Cycle or PCR. Why Calvin cycle is called C3 pathway.
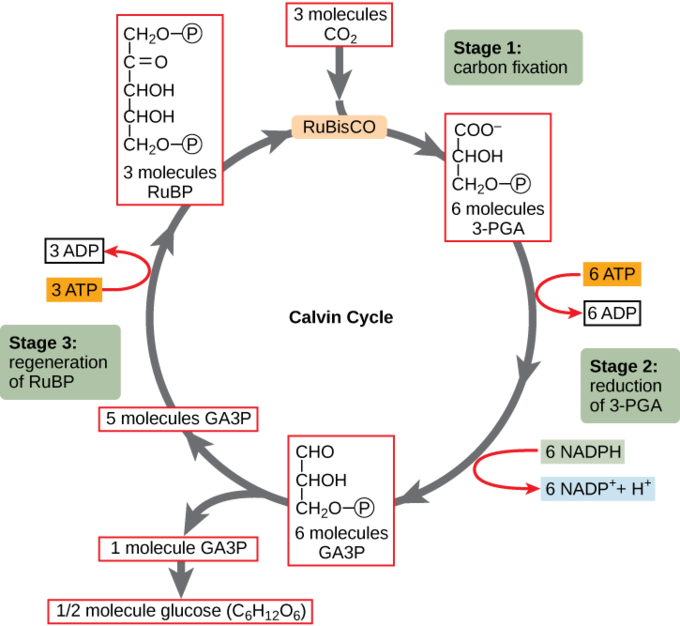
6 fix CO2 onto the pentose ribulose 15-bis-phosphate RuBP. These reactions best known as the Calvin cycle Figure 62. It is called C3 photosynthesis because the first product formed PGA phosphoglycerate contains three carbon atoms.
Calvin along with AA. Calvin Cycle requires the enzyme ribulose-15-bisphosphate carboxylaseoxygenase commonly called. 6 fix CO2 onto the pentose ribulose 15-bis-phosphate RuBP.
Here is a look at the redox reactions that occur during the Calvin cycle. Other Names for the Calvin Cycle. The plants are so-called because of the 4 carbon compound oxaloacetate produced during the pathway.
The cycle uses energy to build a large molecule from smaller ones. The Calvin cycle CalvinBensonBassham CBB cycle reductive pentose phosphate cycle or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms. Calvin or C 3 Cycle or PCR Photosynthetic Carbon Reduction Cycle.
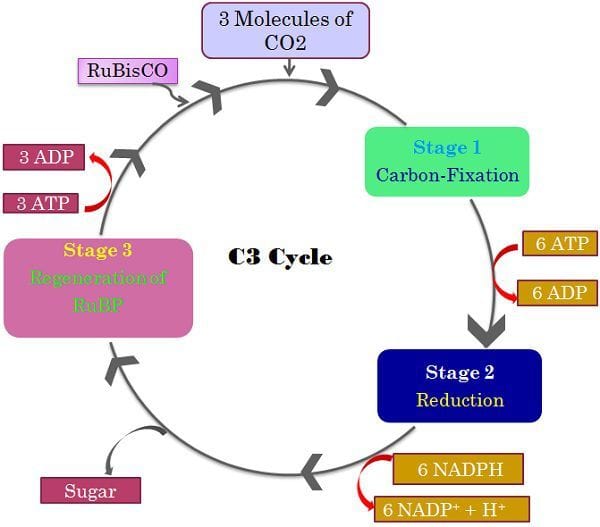
Why is C3 pathway called the C3 pathway. Carbon fixation reduction phase carbohydrate formation and regeneration phase. These reactions are also called the light-independent reactions because they are not directly driven by light.
These reactions best known as the Calvin cycle Figure 62. What percent of plant species use C3 pathways. The Calvin cycle has four main steps.
You may know the Calvin cycle by another name. The plants that undergo the Calvin cycle for carbon fixation are known as C3 plants. Such a pathway is known as the C3 pathway which is also called the Calvin cycle.
In plants carbon dioxide enters the interior of a leaf via pores called stomata and diffuses into the stroma of the chloroplastthe site of the Calvin cycle reactions where sugar is synthesized. 6 fix CO2 onto the pentose ribulose 15-bis-phosphate RuBP. The set of reactions also is known as the dark reactions C3 cycle Calvin-Benson-Bassham CBB cycle or reductive pentose phosphate cycle.
What is another name for Calvin cycle.
5 12c The Calvin Cycle Biology Libretexts
Everything You Need To Know About The Calvin Cycle Biology Junction

What Is The Calvin Cycle C3 Cycle In Class 11
Calvin Or C3 Cycle In Detail Agri Learner

Dark Reaction And Photorespiration Videos Concepts Reactions Types

Why Is Calvin Cycle Also Called C3 Pathway Brainly In

1 Schematic Representation Of The Calvin Cycle The Carboxylation Download Scientific Diagram
Difference Between C3 C4 And Cam Pathway With Comparison Chart Bio Differences

Dark Reaction Calvin Cycle Definition Examples Diagrams

What Do You Understand By Dark Reaction Explain Calvin Cycle C3 Pathway And Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Qforquestions
![]()
Photosynthesis Biosynthetic Pathway Dark Reaction And Difference Between C3 And C4 Plants Flexiprep
Calvin Cycle Steps Calvin Cycle Or C3 Cycle Reductive Pentose Pathway
Calvin Cycle Definition Steps Purpose With Diagram

Dark Reaction Of Photosynthesis Calvin C3 Cycle Qforquestions

Pentose An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

